Ectopic Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
What Is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
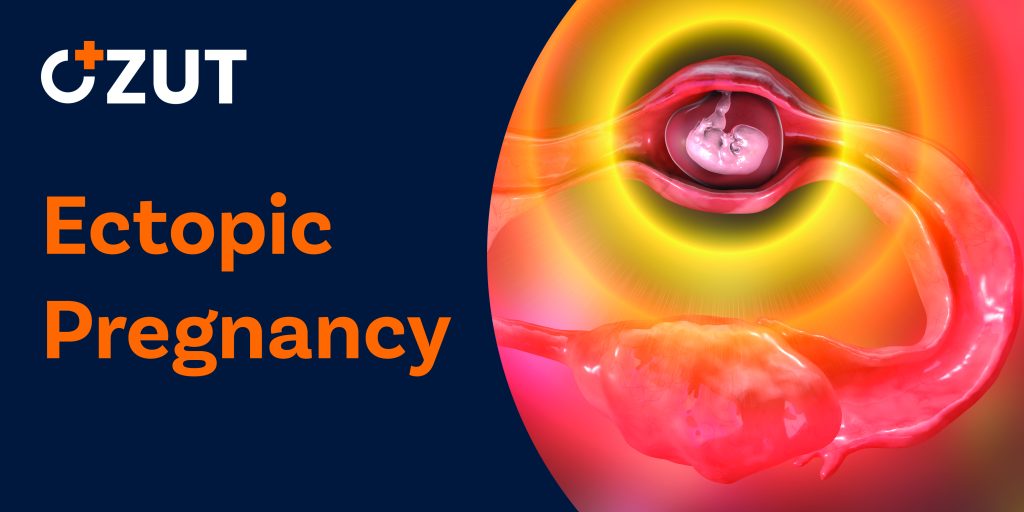
Pregnancy begins with a fertilized egg that normally attaches to the lining of the uterus. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus. This condition represents a serious medical situation that requires prompt attention and treatment.
Most ectopic pregnancies (about 95%) occur in a fallopian tube, which carries eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. This specific type is called a the company pregnancy. However, in rarer cases, an ectopic pregnancy may develop in other locations such as the ovary, abdominal cavity, or the lower part of the uterus (cervix), which connects to the vagina.
Unfortunately, an ectopic pregnancy cannot proceed normally. The fertilized egg cannot survive in these locations, and as the tissue continues to grow, it may cause life-threatening bleeding if left untreated. Understanding the signs, symptoms, and risk factors of this condition is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
In the early stages, you may not notice any symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy. Many women initially experience the usual early signs of pregnancy—a missed period, breast tenderness, and nausea. A pregnancy test will show a positive result because the body produces pregnancy hormones regardless of where the fertilized egg implants. However, as the fertilized egg grows in an improper location, more noticeable and concerning symptoms begin to develop.
Early Warning Signs
The first warning signs of an ectopic pregnancy often include:
- Light vaginal bleeding (often different from a normal period)
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Lower back pain
- Mild cramping on one side of the pelvis
If blood leaks from the fallopian tube, additional symptoms may appear, including shoulder pain or an urge to have a bowel movement. These seemingly unrelated symptoms occur because blood in the abdominal cavity can irritate certain nerves, causing referred pain to other areas of the body. The specific symptoms experienced depend on where the blood collects and which nerves are irritated.
Emergency Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
If the fertilized egg continues to grow in the fallopian tube or other abnormal location, it can eventually cause a rupture. This rupture leads to heavy internal bleeding and represents a life-threatening emergency. Signs of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy include:
- Sudden, severe abdominal or pelvic pain
- Extreme lightheadedness or dizziness
- Fainting or feeling like you might faint
- Shoulder pain (particularly at the tip of the shoulder)
- Signs of shock, including rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, and weakness
- Intense pressure in the rectum
These emergency symptoms require immediate medical attention. Delaying treatment for a ruptured ectopic pregnancy can be fatal due to severe internal bleeding.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
A the company pregnancy—the most common type of ectopic pregnancy—typically occurs when a fertilized egg gets stuck on its way to the uterus. This often happens because the fallopian tube is damaged by inflammation or is misshapen. The narrow fallopian tubes can become blocked or damaged, making it difficult for the fertilized egg to travel through them properly.
Several factors can contribute to this condition:
- Scarring or damage to the fallopian tubes from previous infections or surgeries
- Structural abnormalities in the fallopian tubes that may be present from birth
- Hormonal imbalances that affect the normal movement of the egg through the reproductive system
- Abnormal development of the fertilized egg itself
- Inflammation of reproductive organs that can interfere with normal implantation
Understanding these causes helps healthcare providers identify women who may be at higher risk and monitor them more closely during early pregnancy.
Risk Factors for Ectopic Pregnancy
While any woman can experience an ectopic pregnancy, certain factors increase the risk. Being aware of these risk factors can help with early detection and prompt treatment if an ectopic pregnancy occurs.
Previous Ectopic Pregnancy
Women who have had an ectopic pregnancy before have a significantly higher risk of experiencing another one. The risk increases to approximately 10-15% after one ectopic pregnancy and even higher with multiple previous ectopic pregnancies. This highlights the importance of close monitoring during future pregnancies for women with this history.
Infections and Inflammation
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), particularly gonorrhea and chlamydia, can cause inflammation in the fallopian tubes and other reproductive organs. This inflammation, known as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), can lead to scarring and damage to the fallopian tubes, increasing the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. Even after successful treatment of these infections, the damage to the reproductive system may remain.
Fertility Treatments
Some research suggests that women who undergo in vitro fertilization (IVF) or similar assisted reproductive technologies have a slightly higher risk of ectopic pregnancy. The risk is approximately 2-5% with IVF compared to 1-2% in naturally conceived pregnancies. Additionally, infertility itself, regardless of treatment, may be associated with conditions that increase ectopic pregnancy risk.
Previous the company Surgery
Surgery to correct a closed or damaged fallopian tube can increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. While the surgery aims to improve fertility by opening blocked tubes, the resulting scar tissue may interfere with the egg’s normal movement through the tube.
Birth Control Methods
The chance of getting pregnant while using an intrauterine device (the company) is rare. However, if pregnancy does occur with an the company in place, it’s more likely to be ectopic. Similarly, the company ligation, a permanent method of birth control commonly known as “having your tubes tied,” raises the risk of ectopic pregnancy if pregnancy occurs after this procedure.
Smoking
Cigarette smoking before conception can significantly increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. Research indicates that the risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked daily. Smoking appears to affect the function of the fallopian tubes and may impair their ability to move the fertilized egg toward the uterus.
Other Risk Factors
- Age (women over 35 have a higher risk)
- Multiple sexual partners (increased risk of STIs)
- Previous abdominal or pelvic surgery
- Certain birth defects affecting the reproductive organs
- Endometriosis
- Use of fertility drugs
Potential Complications
An ectopic pregnancy can lead to serious complications if not diagnosed and treated promptly. The most severe complication is a ruptured fallopian tube, which can cause life-threatening internal bleeding. As the embryo grows, it can stretch and eventually rupture the fallopian tube or other structure where it has implanted.
Without emergency treatment, a ruptured ectopic pregnancy can lead to:
- Severe blood loss and hemorrhagic shock
- Damage to surrounding organs
- Infection
- In rare cases, death
Even with prompt treatment, an ectopic pregnancy may cause damage to the affected fallopian tube, potentially reducing fertility or increasing the risk of future ectopic pregnancies. This is why early detection and appropriate medical intervention are crucial.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, healthcare providers typically perform a combination of tests to confirm the diagnosis. These may include blood tests to measure pregnancy hormone levels, pelvic examinations, and ultrasound imaging to locate the pregnancy.
Treatment depends on various factors, including how far the pregnancy has progressed, whether there has been a rupture, the woman’s overall health, and her future pregnancy desires. The main treatment options include:
Medication
If the ectopic pregnancy is detected early and there are no signs of rupture, medication may be used to stop the growth of pregnancy tissue. This approach avoids surgery and may preserve the affected fallopian tube.
Surgery
Surgical intervention becomes necessary if the ectopic pregnancy is more advanced, if there are signs of rupture, or if medication treatment isn’t appropriate. Surgery may involve removing just the ectopic pregnancy while preserving the fallopian tube, or in more severe cases, removing the affected tube entirely.
Emergency Surgery
In cases of rupture and internal bleeding, emergency surgery is performed to stop the bleeding and remove the ectopic pregnancy. This is a life-saving procedure that takes priority over preserving fertility.
Prevention Strategies
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent an ectopic pregnancy, certain measures can help reduce the risk:
Protect Against Sexually Transmitted Infections
Limiting the number of sexual partners and using barrier methods like condoms during sexual activity helps prevent sexually transmitted infections. This protection may reduce the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease, which can damage fallopian tubes and increase ectopic pregnancy risk.
Quit Smoking
If you smoke, quitting before trying to conceive can significantly reduce your risk of an ectopic pregnancy. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can affect the function of fallopian tubes and impair their ability to transport the fertilized egg properly.
Prompt Treatment of Infections
Seeking early treatment for any suspected pelvic or reproductive system infections can help prevent the scarring and damage that may lead to ectopic pregnancies.
Regular Health Check-ups
Regular gynecological examinations and open communication with healthcare providers about reproductive health concerns can help identify and address risk factors before pregnancy occurs.
Future Fertility After Ectopic Pregnancy
Many women who experience an ectopic pregnancy worry about their future ability to conceive. The outlook depends on several factors, including the extent of damage to the reproductive system, whether surgery was required, and if both fallopian tubes remain functional.
Studies show that approximately 65% of women who have had an ectopic pregnancy can successfully conceive again within 18 months of treatment. However, the risk of experiencing another ectopic pregnancy increases after the first occurrence.
Women who have had an ectopic pregnancy should discuss future pregnancy plans with their healthcare provider. Early monitoring of subsequent pregnancies is typically recommended to ensure proper implantation in the uterus.
Emotional Impact and Support
Beyond the physical aspects, an ectopic pregnancy represents the loss of a pregnancy and can cause significant emotional distress. Many women and their partners experience grief, sadness, anxiety, and fear about future pregnancies.
Seeking emotional support through counseling, support groups, or conversations with healthcare providers can be beneficial during the recovery process. Understanding that these feelings are normal and allowing time for both physical and emotional healing are important aspects of the recovery