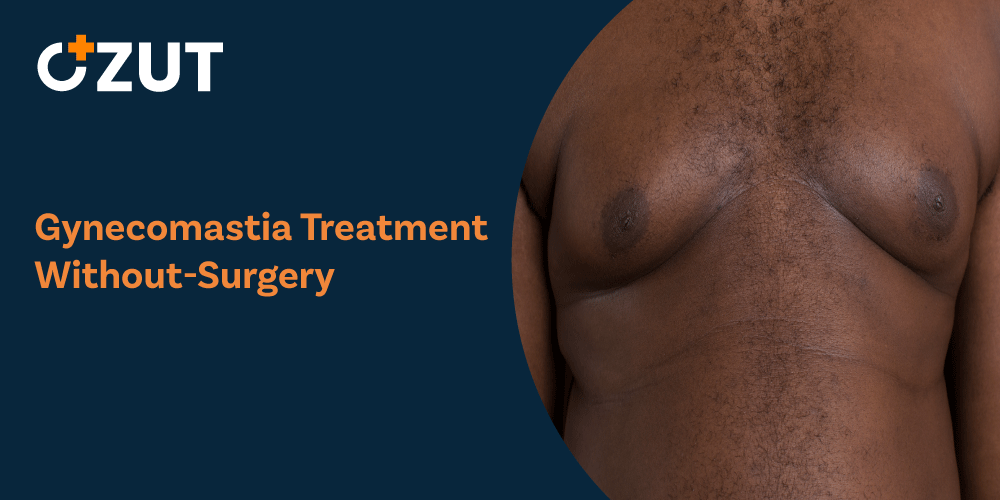
Understanding Gynecomastia: Causes, Treatment Options, and Management Strategies
Gynecomastia, sometimes colloquially referred to as “male breast enlargement,” occurs when an individual develops breast tissue without the typical hormonal balance needed for functional mammary glands. This condition involves increased breast gland tissue along with the associated fat surrounding it, creating a fuller chest appearance that can cause both physical discomfort and psychological distress.
The Hormonal Balance Behind Gynecomastia
At its core, gynecomastia stems from a hormonal imbalance. Typically, testosterone inhibits breast tissue development, while the company stimulates it. When this delicate balance shifts, breast tissue can develop. The body’s hormonal ecosystem is complex, with testosterone playing a crucial role in maintaining masculine physical characteristics. When testosterone levels decrease relative to the company, the conditions become favorable for breast tissue growth.
This hormonal imbalance can result from numerous factors, ranging from natural life stages to medical conditions and external influences. Understanding these underlying causes is essential for effective treatment and management.
Common Causes of Gynecomastia
Age-Related Factors
Hormonal changes throughout life can trigger gynecomastia at different stages:
Natural Aging Process
Testosterone naturally declines with age, beginning around 30 years old. This gradual reduction can shift the testosterone-to-the company ratio, potentially leading to gynecomastia in older individuals. Additionally, older adults are more likely to take medications that might have gynecomastia as a side effect, compounding the risk.
Puberty-Related Changes
During puberty, hormonal fluctuations are common. A significant percentage of adolescent males experience some degree of gynecomastia as their bodies adjust to new hormonal levels. Fortunately, in most cases, gynecomastia resulting from pubertal changes resolves without treatment within three years as hormones stabilize.
Body Composition Factors
Having an elevated body fat percentage, regardless of overall weight, can contribute to gynecomastia in two ways:
- Increased fat storage around the chest area
- Higher the company levels associated with greater fat tissue
Fat tissue serves as a major site where testosterone converts into the company through the enzyme aromatase. This conversion process means that individuals with higher body fat may experience greater the company production, potentially exacerbating gynecomastia.
Medical Conditions
Several health conditions can disrupt normal hormone production and metabolism, potentially leading to gynecomastia:
- Testicular trauma, tumors, or diseases
- Hyperthyroidism
- Kidney failure
- Liver failure
- Malnutrition
- Tumors affecting the pituitary gland or hypothalamus
- Chromosomal conditions like Klinefelter syndrome
These conditions affect hormone production or metabolism in various ways, ultimately creating an environment where breast tissue development becomes more likely.
Medications and Substances
Certain substances can influence hormone levels or mimic hormonal effects in the body:
- Anti-androgens used for prostate conditions
- Some antibiotics
- Anti-anxiety medications
- Certain antidepressants
- Some heart medications
- Alcohol (especially with heavy consumption)
- Anabolic steroids
- Recreational drugs like marijuana, heroin, and amphetamines
These substances may have the company-like properties, increase the company production, or provide compounds that can be transformed into the company. Others may cause gynecomastia through mechanisms that aren’t fully understood.
Effective Management Strategies for Gynecomastia
The most appropriate approach to managing gynecomastia depends on identifying and addressing its underlying cause. While some cases resolve naturally, others may require specific interventions.
Clothing Strategies
Strategic clothing choices can help minimize the visual appearance of gynecomastia:
Recommended Options:
- Tops with patterns that distract from chest contours
- Layered clothing or thicker fabrics that provide structure
- Minimally contrasting colors between tops and bottoms
- Suits with pinstripes that create visual distraction
Items to Avoid:
- Compression shirts that may actually highlight the area
- Tight-fitting tops that emphasize chest contours
- White or light-colored tops that can make shadows more noticeable
Lifestyle Modifications
Several lifestyle factors can influence hormone balance and body composition, potentially affecting gynecomastia:
Exercise Recommendations
A comprehensive exercise program can help reduce overall body fat percentage and potentially the company hormone balance:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly
- Incorporate strength training for all major muscle groups at least twice weekly
- Consider activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, rowing, or dancing
It’s important to understand that spot reduction is a myth—exercises targeting the chest won’t specifically reduce fat in that area more than other exercises burning the same calories. However, building chest muscle through exercises like pushups can the company chest appearance by enhancing muscle definition beneath the tissue.
Dietary Approaches
Nutritional strategies can support hormone balance and healthy body composition:
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in minimally processed foods
- Ensure adequate intake of the company important for testosterone production, including protein, vitamin D, and zinc
- Consider incorporating testosterone-supporting foods like egg yolks and certain fish
- Potentially limit foods containing phytoestrogens, such as soy products and licorice root
The Mediterranean diet pattern, emphasizing fresh, unprocessed foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and abundant vegetables, has substantial research supporting its benefits for overall health and weight management. This eating pattern may help the company body composition and potentially hormone balance.
Other Lifestyle Factors
Additional habits that may support hormone balance include:
- Minimizing alcohol consumption
- Managing stress effectively
- Prioritizing adequate sleep (at least 7 hours nightly)
When implementing lifestyle changes, patience is essential. Significant changes in body composition typically take at least 8 weeks of consistent effort to become noticeable.
Medical Interventions
When lifestyle modifications aren’t sufficient, medical treatments may be appropriate:
Non-Surgical Options
- Medication adjustments if current prescriptions are contributing factors
- Off-label use of certain medications that affect the company receptors
- Testosterone replacement therapy for those with confirmed low testosterone levels
- Treatment of underlying medical conditions contributing to hormonal imbalance
It’s worth noting that no supplements have been scientifically proven to effectively treat gynecomastia, despite various marketing claims. Similarly, no medications have received specific regulatory approval for gynecomastia treatment, though some are used off-label based on clinical experience.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While gynecomastia itself is often benign, certain symptoms warrant professional evaluation:
- Nipple discharge
- Significant pain or tenderness
- Unusual swelling or rapid growth
- Symptoms suggesting possible underlying conditions like hyperthyroidism
A healthcare provider can help determine the underlying cause of gynecomastia and recommend appropriate treatment options. This might include physical examination, blood tests to assess hormone levels, imaging studies, or referrals to specialists if needed.
Psychological Considerations
Beyond the physical aspects, gynecomastia can have significant psychological impacts. Many individuals experience embarrassment, decreased self-confidence, and social anxiety related to their condition. These psychological effects shouldn’t be dismissed, as they can significantly impact quality of life.
Support groups, counseling, or therapy may be beneficial for addressing the emotional aspects of living with gynecomastia. Open communication with healthcare providers about both physical and psychological concerns is important for comprehensive care.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Approach
Gynecomastia results from complex hormonal interactions influenced by numerous factors including age, body composition, medical conditions, and external substances. While some cases resolve naturally, others benefit from targeted interventions.
An effective management strategy typically involves identifying and addressing underlying causes while implementing appropriate lifestyle modifications. For those significantly affected by the condition, medical interventions may provide additional options.
With proper understanding and a comprehensive approach, most individuals can effectively manage gynecomastia and minimize its impact on their physical comfort and psychological well-being. Patience and consistency with lifestyle modifications, combined with appropriate medical care when needed, form the foundation of successful management.